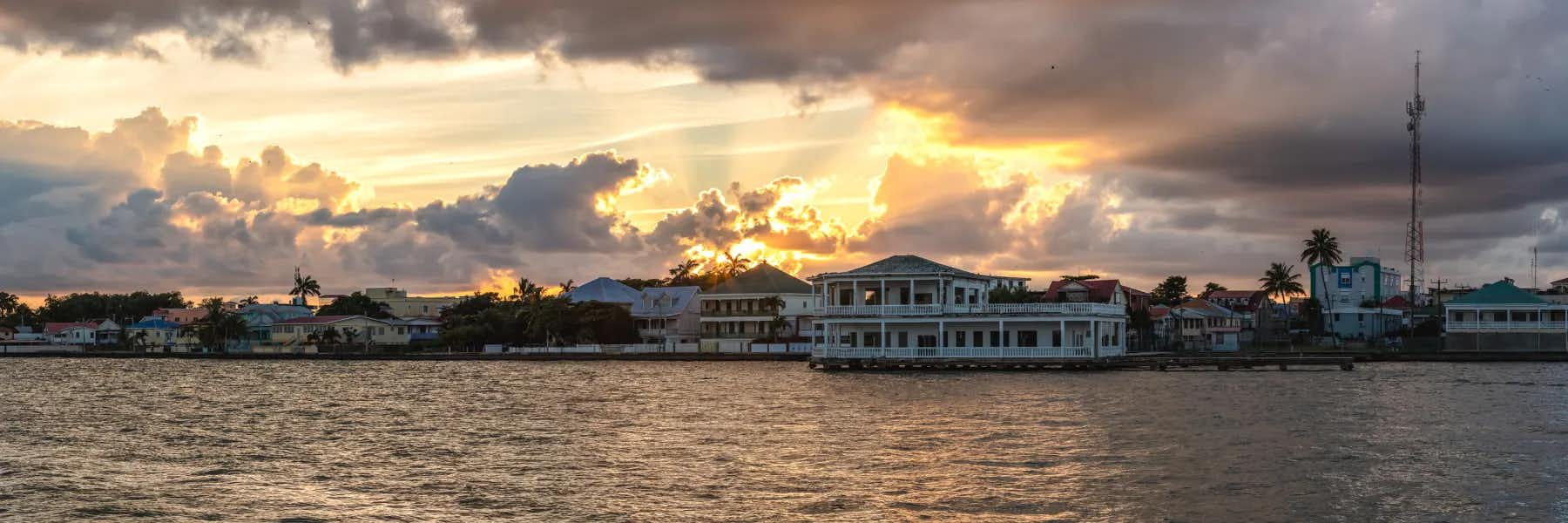
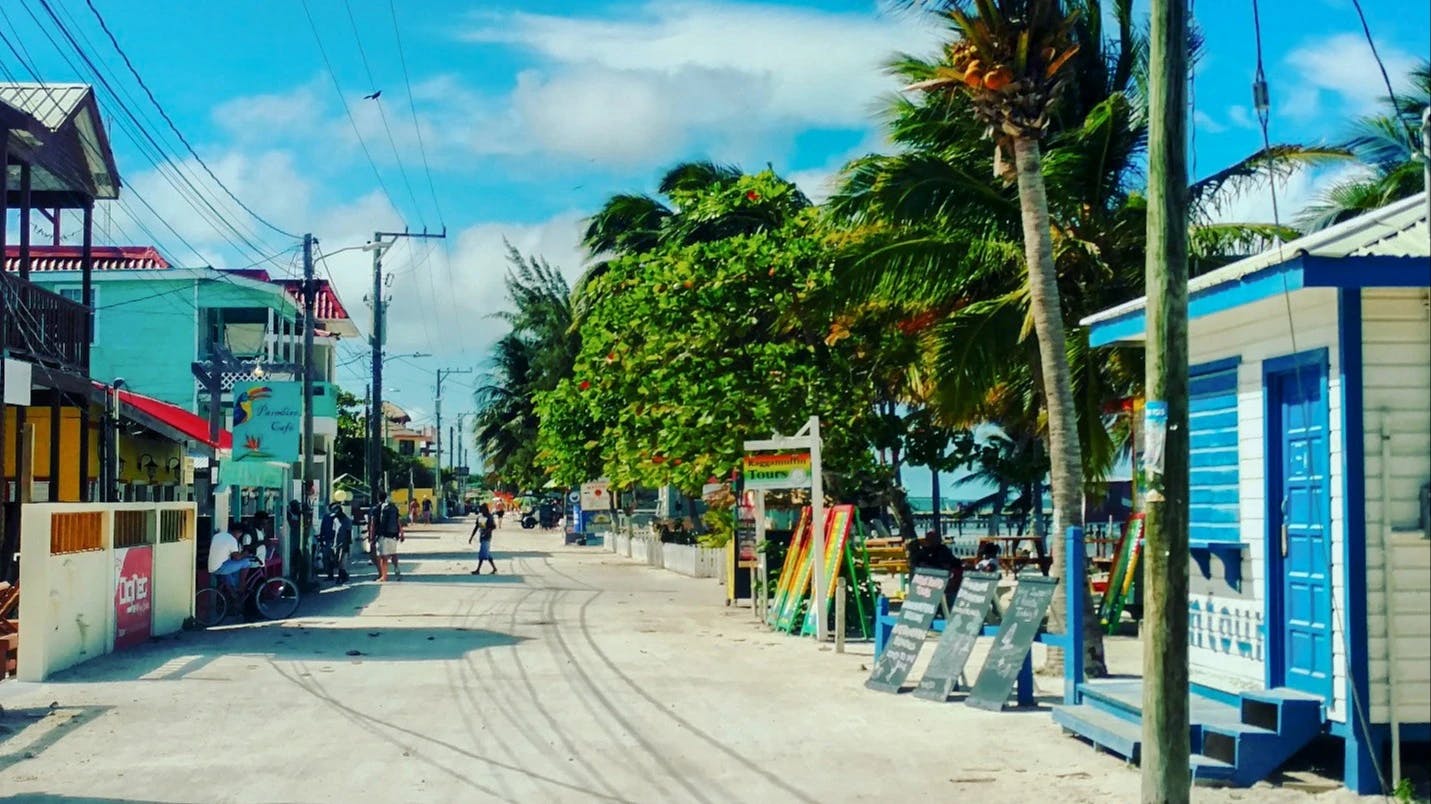
Learning from its colonial past, the government of Belize has sought to preserve the country’s natural beauty and resources while encouraging tourism and the immigration of new residents with the means to support themselves. Although English is the official language of Belize, there are many places inthe country where Spanish and English are both spoken. English remains the country’s dominant language, especially since tourism has become the fastest growing source of income for Belize. But the trend toward Latin American culture will also continue in music, language, food, and lifestyle.
Tourism is the number one foreign exchange earner in this small economy, followed by exports of sugar, bananas, citrus, marine products, and crude oil.
The government's expansionary monetary and fiscal policies, initiated in September 1998, led to GDP growth averaging nearly 4% in 1999-2007, but GPD growth has averaged only 2.1% from 2007-2016, with 2.5% growth estimated for 2017. Belize’s dependence on energy imports makes it susceptible to energy price shocks.
Although Belize has the third highest per capita income in Central America, the average income figure masks a huge income disparity between rich and poor, and a key government objective remains reducing poverty and inequality with the help of international donors. High unemployment, a growing trade deficit and heavy foreign debt burden continue to be major concerns. Belize faces continued pressure from rising sovereign debt, and a growing trade imbalance.
Labor force: 120,500
Labor force by occupation:
Agriculture: 10.3%
Industry: 21.6%
Services: 68%
Exports: $457.5 million
Export partners: U.K. 33.9%, U.S. 22%, Jamaica 6.7%, Italy 6.4%, Barbados 5.9%, Ireland 5.5%, Netherlands 4.3% (2017)
Export commodities: Sugar, bananas, citrus, clothing, fish products, molasses, wood, and crude oil.
Imports: $845.9 million
Import commodities: Machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods; fuels, chemicals, pharmaceuticals; food, beverages, and tobacco.
Source: CIA The World Factbook
Get Your Free Belize Report Here
Get Your Free Belize Report Here
Learn more about Belize and other countries in our daily postcard e-letter. Simply enter your email address below and we'll send you a FREE report - Belize: The Friendly, Affordable Caribbean Nation.

By submitting your email address, you will receive a free subscription to IL Postcards and special offers from International Living and our affiliates. You can unsubscribe at any time, and we encourage you to read more about our Privacy Policy.